What is solé?
Solé (pronounced so-lay) is a mineral tonic made by dissolving pure salt (such as Kalahari Salt), into water.
It was introduced by the book Water and Salt: The Essence of Life.
Because it contains salt and trace amounts of other electrolytes, solé functions similarly to electrolyte drinks that people take to replenish lost minerals and to rehydrate the body.
Make your own solé;

By dissolving pure salt into water until the water becomes fully saturated and cannot absorb more salt.
Serve the tonic by mixing a teaspoon of the liquid into your morning glass of water.
By dissolving pure salt into water until the water becomes fully saturated and cannot absorb more salt.
Serve the tonic by mixing a teaspoon of the liquid into your morning glass of water.
While most of its advocates take it in the morning, you can also use solé to help rehydrate the body after exercise or on hot days to replace the water and electrolytes lost in perspiration.
What are the benefits?
Some of solé’s most ardent advocates claim that drinking the tonic provides many benefits:
from better sleep and more energy to fewer allergies and better mood
We know that salt performs a wide variety of functions in the human body and is essential for health when taken in appropriate amounts.
Accordingly, drinking solé or salting your foods to taste can help support systemic wellness.
• Mineral-rich salt supports hydration. Your body’s ability to hydrate effectively depends on salt and other electrolytes
• Salt supports Ph balance. Salt and other electrolytes support pH balance and help transport nutrients to cells
• Salt supports digestion. The chloride in salt is necessary for producing stomach acid, and salt itself supports the transport of nutrients in the small intestines
• The right amount of salt supports metabolic health. Low-salt diets may aggravate insulin resistance
• Unrefined salt contains a wide variety of minerals. In addition to sodium chloride, minimally processed salts contain various minerals in trace amounts, including calcium, sulfur, potassium, magnesium and iron.
Rheumatism
Rheumatism is a broad and somewhat outdated term that has been historically used to describe various conditions characterized by pain and inflammation in the muscles, joints, and connective tissues. However, in modern medicine, the term “rheumatism” is no longer used as a specific diagnosis because it doesn’t refer to a single, well-defined medical condition. Instead, healthcare professionals use more specific and accurate terminology to describe the various disorders that can affect the musculoskeletal system.
Gout
This is a form of arthritis where severe pain, redness, and tenderness in the joints is experienced. Gout attacks can last from a few days to a couple of weeks. Gout can affect both sexes and all age groups although it is not often seen in those under 40, while it is most commonly seen in men over 60.
Joint pain
Joint pain refers to discomfort, soreness, or aching sensations that occur in the areas where two or more bones meet and are connected by various tissues, such as ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. Joints play a crucial role in facilitating movement and providing structural support to the body.
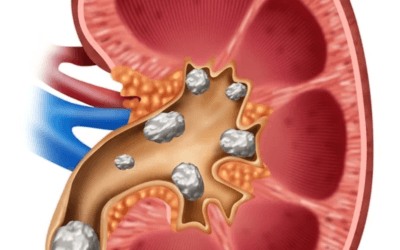
Kidney stones
Kidney stones (renal calculi) are mineral salt accumulations that lodge anywhere along the course of the ureters (the tubes that carry urine to the bladder). These deposits are composed of calcium phosphate, calcium oxalate, ammonium phosphate, calcium carbonate, and uric acids or urates. This condition may affect adults of both sexes usually in those over 30. More men than women are prone to these attacks. Kidney stones are hard mineral and salt deposits that form in the kidneys. The symptoms of kidney stones can vary depending on their size, location, and whether they are causing a blockage or irritation. Here are the common symptoms associated with kidney stones:
Insulin Resistance – Source of Most Chronic Disease
One of the significant threats to global health in the 21st century is insulin resistance, which is the key factor in the development of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, fatty liver disease, neurogenerative disease, and obesity-associated cancers. Understanding the molecular basis for insulin resistance leads to specific therapy that helps prevent this common disorder, and we now have a medicine that cleans up the mess in the vascular system after years and even decades of our bodies’ being under the sway of insulin resistance.
How to recognize the real Zechstein Magnesium chloride product
We sell magnesium chloride from the world-unique Zechstein Source in Veendam, the Netherlands. For Zechstein Minerals, our source means the connection to the Zechstein Sea. The Zechstein Sea was an inland sea that stretched over what is now North-western Europe about 250 million years ago (in the Permian era). In this sea, the evaporite deposits (layers after evaporation) of the Zechstein era were formed. The Zechstein Sea was connected to the Tethys Ocean by close connections in the south.