Rheumatism is a broad and somewhat outdated term that has been historically used to describe various conditions characterized by pain and inflammation in the muscles, joints, and connective tissues. However, in modern medicine, the term “rheumatism” is no longer used as a specific diagnosis because it doesn’t refer to a single, well-defined medical condition. Instead, healthcare professionals use more specific and accurate terminology to describe the various disorders that can affect the musculoskeletal system.

Gout
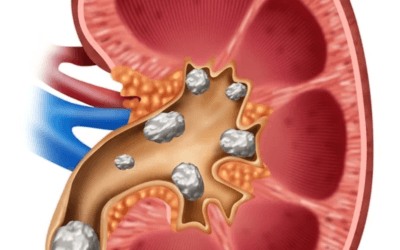
This is a form of arthritis where severe pain, redness, and tenderness in the joints is experienced. Gout attacks can last from a few days to a couple of weeks. Gout can affect both sexes and all age groups although it is not often seen in those under 40, while it is most commonly seen in men over 60.
Crystalline sodium urate deposition in the soft tissues and cartilage may produce nodules known as tophi, these may reach a point where they cause the joints to completely seize. Repeated bouts of gout over a long period of time can cause permanent joint damage. Severe pain, inflammation, swelling, and tenderness of affected joints.
It is most often seen in the big toe joint but other joints including the ankle, knee, mid-foot, wrist, and fingers are also affected. Because uric acid crystallizes at lower temperatures, it might explain why gout is often located in the extremities like the big toe joint. Lifestyle, dietary changes, and supplementation
Nutrients and supplements:
1. Gout remedy – for gout of all types.
2. Buffered Vit C – helps to lower serum uric acid levels.
3. Vit B Complex – required for proper
4. Zinc – for tissue repair.
5. D.M.S.O – applied topically may be helpful for flare-ups reducing swelling and relieving pain.
6. Potassium – to maintain a proper mineral balance
7. Kelp – contains proteins and minerals that help reduce serum uric acid. Gout is caused by an imbalance of uric acid (sodium urate) in the blood, tissue, and urine. The deposit of uric acid crystals in the joints causes inflammation, swelling, and pain. Gout may be passed on genetically.
The following put you at risk for developing gout:
1. Being obese
2. Hypertension
3. Having Insulin resistance
4. Metabolic syndrome
5. Diabetes
6. Poor kidney function
7. Nutrient deficiencies; A vitamin B5 deficiency may produce high levels of uric acid. Animal studies have also shown that a deficiency of vitamin A can cause gout, while vitamin E deficiency may also be responsible for high levels of uric acid.
8. People who have been on antibiotics for long periods or people who have frequent candida infections may often have increased levels of uric acid in their blood. Feelings of impatience and anger, the desire to dominate due to feeling of control or feelings of disempowerment. A diet low in purines is indicated (purines are organic compounds that contribute to uric acid formation).
Some valuable tips;
1. Avoid the following high purine foods; organ meats (such as liver, kidneys), sweetbreads, anchovies, shellfish, asparagus, mincemeat, mushrooms, lentils, dry peas, dry beans, and sardines. Eliminate homogenized milk as this may be a source of xanthene oxidase which can increase levels of uric acid. Also, try to avoid anything containing Vitamin B3, alcohol, coffee, tea, cocoa, fizzy drinks, and refined carbohydrates
2. Foods with low purine content include; green vegetables, nuts, most vegetables, cereals, fruits, and eggs. Therapeutic foods include: apples, black currants, watercress, kale, strawberries, dandelion greens, potato broth, chicory, cherries, blueberries, raspberries, parsnips, celery, olives, rye, lima beans, rice bran, bananas, sprouts, watercress, apples
3. Drink plenty of fluids to dilute the contents of the blood, this will ensure that uric acid has less chance of precipitating out of the blood and will promote excretion of uric acid.
4. A Low-fat diet of unsaturated fats is indicated.
5. Avoid alcohol as this increases the production of uric acid and reduces uric acid elimination. Musculoskeletal System Gout remedy (tinc), Buffered Vit C (caps), Vit B Complex (tabs), Zinc (tabs), D.M.S.O
Article Source Link: https://natra-heal.co.za/gout/
Showing 1–12 of 17 resultsSorted by latest
-

Professional Holistic Body Analyser
R88 000,00 -

Hunter Pathogen Body Scanner
R46 900,00 -

Quantum Bacterial Pathogen Scanner
R34 000,00 -

Traditional Quantum Magnetic Analyzer
R6 975,00 -

Set of low-intensity hand terminals Rife Applicator
R200,00 -

Comfi Belt with double accelerated areas
R1 600,00 -

Small Comfi Patch (mat) with lead wire
R900,00 -

Medium-sized Comfi Mat
R1 500,00 -

Foot Massage Mat and Machine
R450,00 -

TWIN Wave Rife Machine
R9 800,00 -

Majic Wave Rife Massage Machine
R8 500,00 -

Value Package 08
R76 000,00